Sclerotherapy & Glue Injection
Injection sclerotherapy and glue injection:
A sclerosent or Glue injected in the abnormal or bleeder vessel to arrest and prevent bleeding.
A sclerosent is used for esophageal and occasionally in Gastric Varices and some ulcers bleeders.
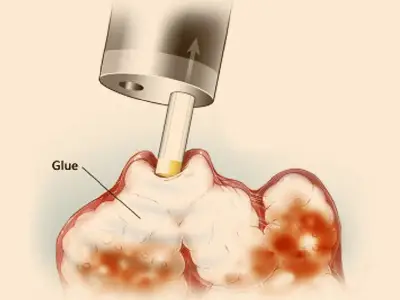
Glue is injected only in Gastric or Ectopic Varices.
The procedure involves the passage of an endoscope and injection of a sclerosing agent into or around esophageal varices or a bleeder vessel in ulcer.
Sclerotherapy:
- Purpose: Sclerotherapy is primarily used to treat small to medium-sized varicose veins and spider veins (telangiectasias). It’s also occasionally used for vascular malformations and hemorrhoids.
- Procedure: During sclerotherapy, a special solution (sclerosant) is injected directly into the affected vein using a fine needle. This solution irritates the inner lining of the vein, causing it to collapse and eventually close off.
- Results: Over time, the treated vein becomes fibrous tissue and is absorbed by the body, while blood is rerouted to healthier veins. This leads to improved blood circulation and alleviation of symptoms associated with the diseased veins.
Glue Injection (VenaSeal Closure System):
- Purpose: The glue injection procedure, often referred to as the VenaSeal Closure System, is used to treat varicose veins, specifically the great saphenous vein (GSV).
- Procedure: In this method, a medical-grade adhesive (glue) is injected into the diseased vein through a catheter. The glue quickly seals the vein shut, preventing blood from flowing through it.
- Results: The treated vein is closed off and eventually absorbed by the body. Blood is rerouted through healthier veins. This procedure is less dependent on irritation like sclerotherapy and often leads to less discomfort and bruising for the patient.
Key differences between the two procedures:
- Agent Used: Sclerotherapy uses a liquid sclerosant, whereas glue injection uses a medical adhesive (glue) to seal the vein.
- Procedure Complexity: Glue injection is generally considered easier to perform, as it relies on the simple sealing action of the glue, while sclerotherapy may require more precise injection techniques.
- Recovery and Side Effects: Sclerotherapy may cause temporary discomfort, bruising, and skin discoloration. Glue injection is often associated with fewer side effects and a quicker recovery.
- Effectiveness: Both procedures can be effective in treating varicose veins, but the choice between them may depend on the size and location of the affected veins, as well as the patient’s overall health.
It’s important to note that the choice between sclerotherapy and glue injection, or any other treatment, should be made after a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider who specializes in venous disorders. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors, including the extent of the condition and the patient’s medical history.